Tears have fascinated humanity since antiquity, appearing in various forms of art and literature throughout history… See more →
Do you experience any of these symptoms?
Tears have fascinated humanity since antiquity, appearing in various forms of art and literature throughout history. Understanding the lacrimal system is crucial for maintaining eye health. There are three basic types of tears:
Each type of tear plays a vital role in protecting and maintaining our eyes.
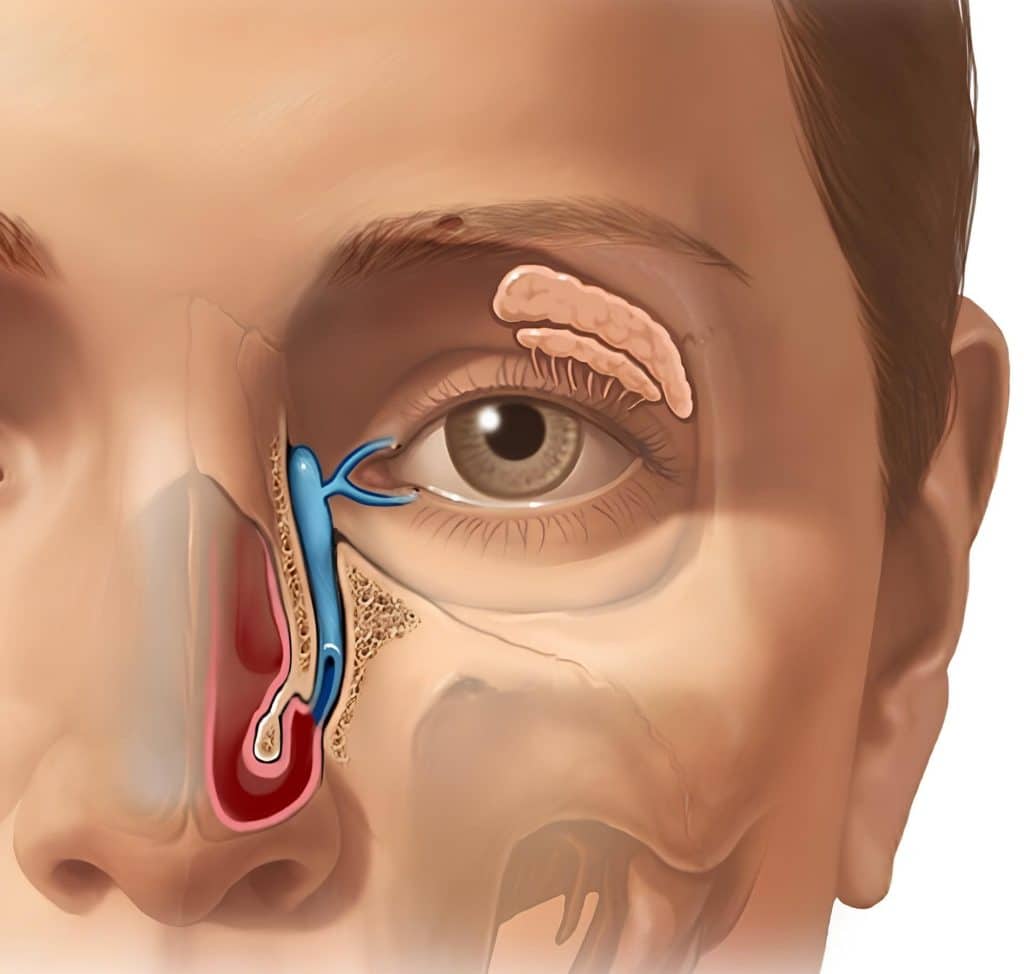
The lacrimal gland, located at the upper outer corner of the eye socket (orbit), is responsible for producing 90% of our tears. The remaining 10% comes from smaller accessory glands in the eyelids.
Tears leave the eye’s surface through two small openings called lacrimal puncta, one in each eyelid. These openings lead to the lacrimal sac, which connects to a duct that carries tears into the nasal cavity. Several valves along this pathway prevent fluid from flowing back into the eye.
When we produce excess tears, such as during emotional crying or in response to irritants, the nose may run as tears drain through the nasolacrimal duct. If tear production exceeds the drainage capacity, tears will overflow onto the cheeks. This overflow is medically termed “epiphora.”
Persistent watery eyes, or epiphora, can significantly impact daily activities such as reading, driving, walking outdoors, watching television, or working on a computer. This condition may result from either excessive basal tear production or insufficient drainage through the lacrimal system.
In our practice, we primarily focus on cases involving insufficient tear drainage, as these are the most common referrals we receive.
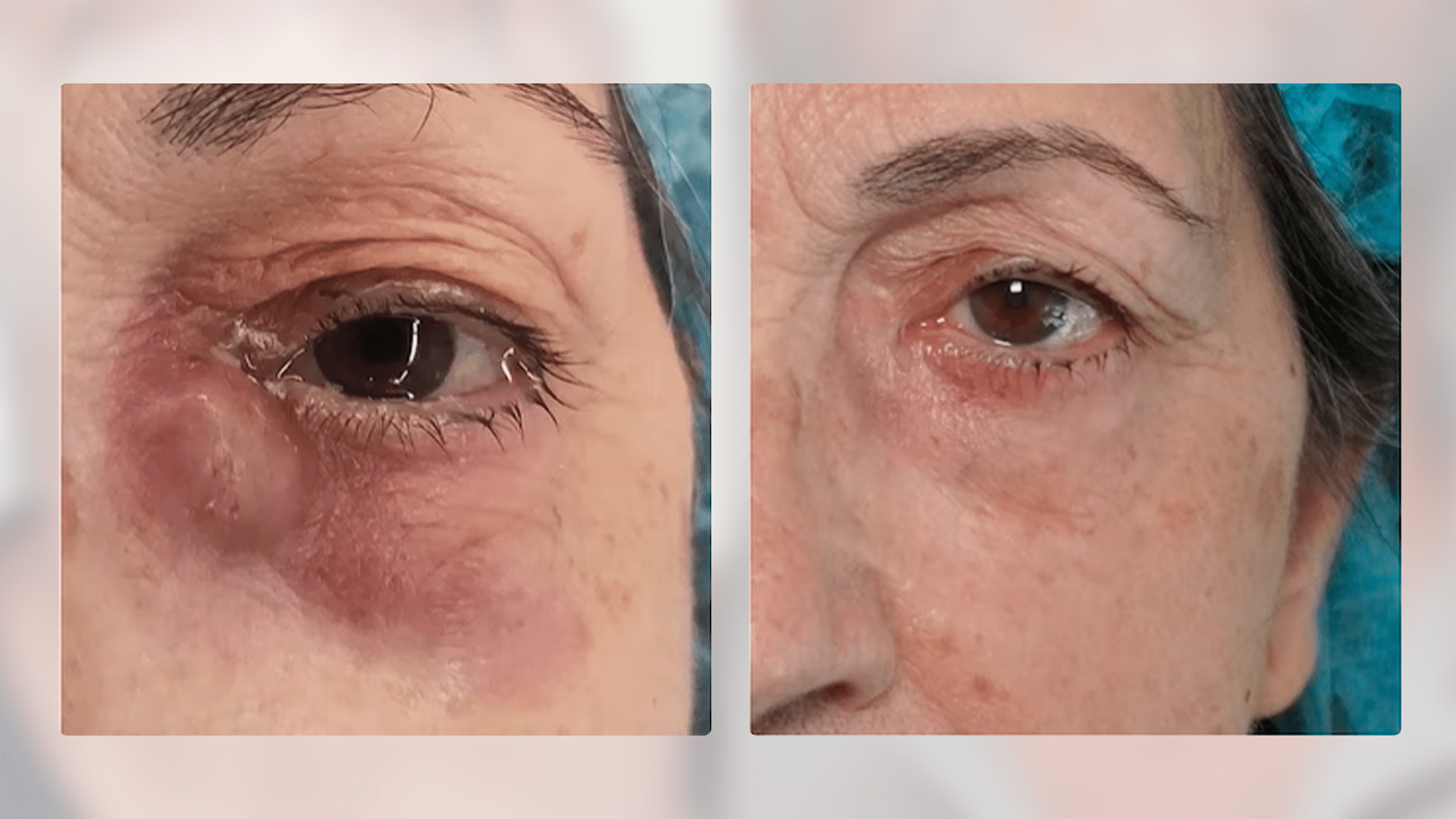
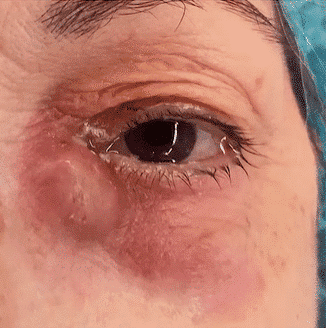
Dacryocystitis is a condition resulting from an obstruction in the nasolacrimal system. This blockage leads to tear stagnation and epiphora, creating an environment conducive to bacterial growth and debris accumulation, ultimately causing a local infection.
Obstructions can occur at any point in the nasolacrimal system due to various factors:
Dacryocystitis typically affects adults over 40 years old. Interestingly, about 70% of cases occur in females, likely due to their naturally narrower lacrimal ducts.
For acute episodes of dacryocystitis, antibiotic therapy is often the first line of treatment. This helps combat the infection and reduce inflammation in the lacrimal system.
Chronic dacryocystitis typically requires surgical management. Our team includes an ophthalmologist for a comprehensive evaluation.
The primary surgical treatment for chronic dacryocystitis is dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR). This procedure is usually performed under general anesthesia and can be done using one of two approaches:
During the surgery, a silicone tube is placed in the newly created lacrimal passage. This tube remains in place for several weeks to prevent re-occlusion and ensure proper healing.
In cases where restoring the natural duct is not possible (due to trauma, oncological issues, or highly fibrotic ducts), an alternative solution is to create a new drainage channel. This is done by inserting a Jones tube in the inner corner of the eye, bypassing the blocked lacrimal system.
Patients typically leave the hospital on the same day or the day after surgery. To prevent unnecessary nose bleeding, it’s crucial to avoid strenuous activities during the initial recovery period.
For patients who are not candidates for general anesthesia, there are alternative surgical approaches and management strategies available. These are tailored to the individual patient’s needs and overall health status.

DCR stands for Dacryocystorhinostomy. It’s a surgical procedure to treat blocked tear ducts by creating a new drainage pathway for tears.
Typically, DCR surgery takes about 1 to 2 hours, depending on the specific technique used and individual patient factors.
Yes, DCR is usually performed under general anesthesia, but in some cases, it can be done under local anesthesia with sedation.
Most patients can return to normal activities within 1 to 2 weeks, but full recovery may take up to 6 weeks.
As with any surgery, there are some risks, including infection, bleeding, and scarring. However, complications are generally rare when performed by an experienced surgeon.
External DCR may leave a small scar near the inner corner of the eye, which usually fades over time. Endoscopic DCR leaves no external scar.
DCR has a high success rate, typically around 90-95% in resolving tear duct blockage symptoms.
Living with persistent watery eyes doesn’t have to be your new normal. Whether you’re struggling with constant tearing, recurring infections, or the social discomfort that comes with epiphora, there are solutions available.
Remember:
Don’t let watery eyes hold you back from enjoying life to the fullest. Our team of experienced ophthalmologists and surgeons specializes in diagnosing and treating lacrimal pathway disorders. We’re here to provide personalized care and cutting-edge treatments tailored to your unique needs.
Ready to say goodbye to watery eyes?
Take the first step towards clearer vision and greater comfort. Contact us now to book your appointment and start your journey to healthier, happier eyes.
Your eyes deserve the best care possible. Let us help you see the world clearly again, without the inconvenience of constant tearing.