Visit us in Lisbon or Évora to discover how our expertise can help you achieve your desired natural and harmonious results, keeping your eyelid functions.
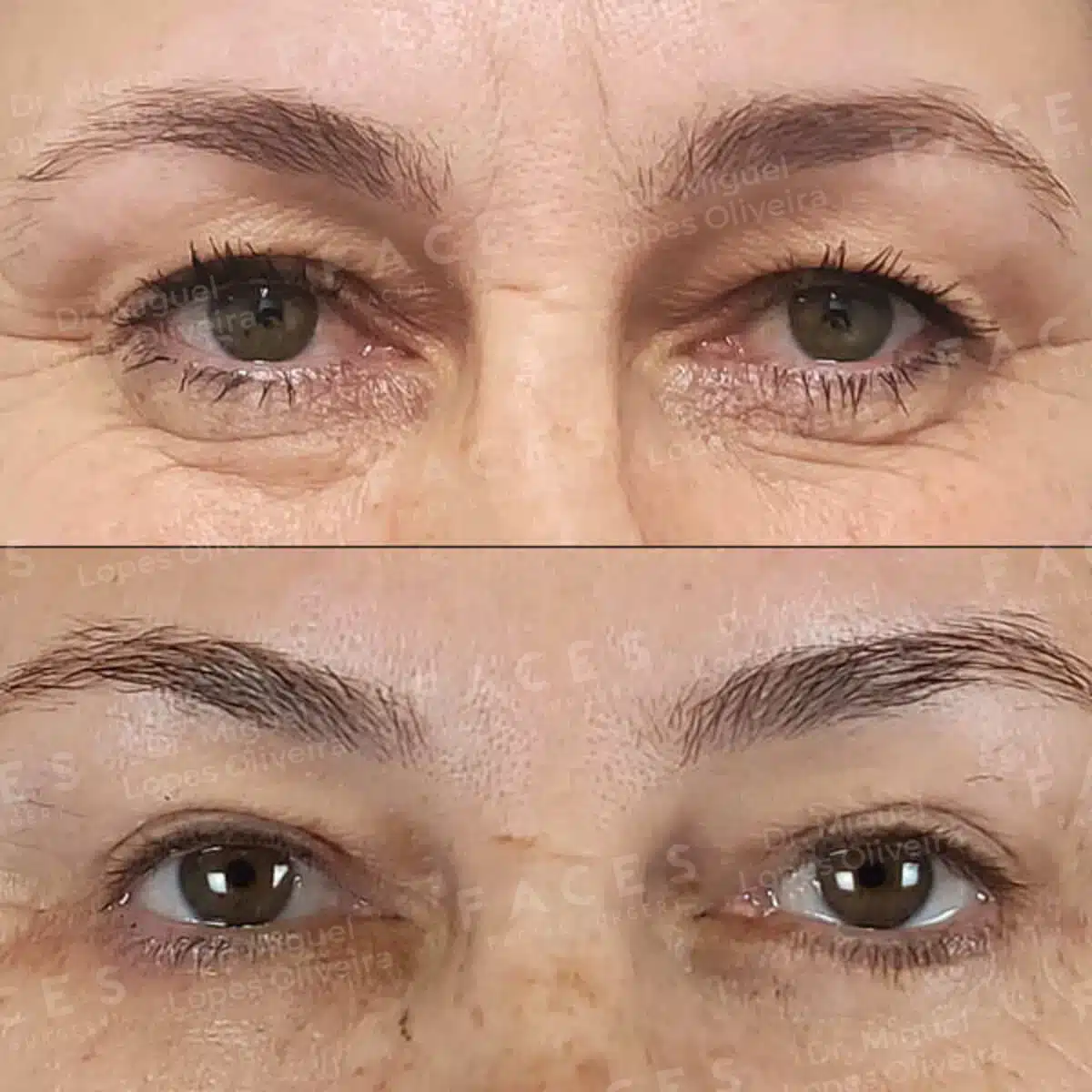
Lower blepharoplasty is a surgical procedure designed to correct under-eye bags, puffiness, and lower eyelid laxity. In Lisbon and Évora, patients frequently seek lower eyelid surgery to restore a rested appearance and address persistent eye bags that do not improve with skincare or non-surgical treatments.
Eye bags are often caused by fat prolapse, skin laxity, or a combination of both. Lower blepharoplasty allows precise correction of these anatomical changes while preserving eyelid function and achieving natural, harmonious results.
Lower blepharoplasty (lower eyelid surgery) is a procedure that treats under-eye bags by removing or repositioning protruding fat and, when necessary, tightening excess skin.
Depending on the clinical findings, surgery may be performed using:
• A transconjunctival approach (internal incision, no visible scar)
• A subciliary approach (fine incision just below the eyelashes)
• Fat repositioning techniques to smooth the tear trough
• Conservative skin tightening when required
The objective is not simply to remove fat, but to restore smooth contour between the lower eyelid and cheek.
You may be a candidate if you have:
• Persistent under-eye bags
• Puffiness that worsens with fatigue
• Lower eyelid laxity
• Hollowing or tear trough deformity
• A tired or aged appearance despite adequate rest
In some cases, lower eyelid changes may also contribute to ocular irritation or incomplete eyelid closure, requiring careful evaluation.
Common causes include:
• Age-related weakening of the orbital septum
• Fat prolapse
• Skin laxity
• Genetic predisposition
• Fluid retention
Accurate diagnosis is essential, as treatment must be tailored to the specific anatomical cause rather than applying a one-size-fits-all approach.
We strongly recommend to perform lower blepharoplasty under general anaesthesia for patient confort, since it usually address deep tissues, such as fat bags. Local anesthesia with or without sedation might be appropriate for skin surgery (superficial surgery) such as wrinkles removal (removal of excess skin).
Key principles include:
• Preservation of eyelid support structures
• Conservative fat removal or repositioning
• Avoidance of over-resection
• Respect for eyelid-cheek transition
• Symmetry and functional integrity
Surgery usually takes 60–90 minutes, depending on complexity.
When a transconjunctival approach is used, there is no visible external scar.
Most patients experience swelling and bruising for 10–14 days.
Typical recovery timeline:
• Days 1–3: swelling, bruising and mild discomfort
• Days 5–7: significant reduction in bruising. You can return to your computer related work, ensuring resting periods each 30min.
• 10–14 days: return to social activities
• 4–6 weeks: refined contour and natural appearance.
Usually a lower blepharoplasty is combined with an upper eyelid surgery as well, since the inferior eyelid lateral canthus positioning (canthopexy/canthoplasty) is made through an upper lid incision. Therefore, upper eyelid excessive skin or lateral contour is usually addressed at this time as well.
Results are long-lasting, especially when fat repositioning techniques are used. Age-related change will keep ongoing, in particular when smoking or getting excessive sun exposer.
With transconjunctival surgery, there is no external scar. When a skin incision is necessary, it is placed discreetly beneath the eyelashes.
Natural ageing continues, but properly performed surgery provides long lasting improvement.
Discomfort is generally mild and controlled with medication.